3D printing is among the modern technologies that have transformed the world of industrial manufacturing. Originally regarded as a technique for prototyping and production of complex models, this groundbreaking technology has expanded its reach across diverse industries. Its cost-effective and flexible solutions have particularly revolutionized mold manufacturing, an industry known for its complex and time-consuming processes. The integration of 3D printing has not only streamlined production but also opened up opportunities for producing complex designs, minimized waste, and accelerated time-to-market capabilities.
The main purpose of mold manufacturing is to produce plastic components with high precision, repeatability, and quick turnaround time. With the introduction of 3D printing, the whole game is changing. 3D printing is challenging traditional norms and setting a new benchmark for what’s possible injection molding of plastics. In this article, we’ll explore how this technology is reshaping the mold manufacturing process.
This Guide Covers:
- Benefits of 3D Printing in Mold Manufacturing
- Challenges and Limitations
- Case Studies and Applications
- Conclusion
Benefits of 3D Printing in Mold Manufacturing
3D printing has brought many benefits in the field of mold manufacturing. These include:
– Speed. Integrating 3D printing into mold manufacturing increases the speed of mold design and production remarkably. Traditionally, creating molds involved multiple time-consuming stages, such as CNC machining or manual crafting, from design to finish. For complex designs, this process could be laborious. However, with 3D printing, molds can now be produced directly from digital files without the need for intermediaries or extra time. This quick production enables businesses to swiftly respond to market demands and adapt to design changes promptly, ultimately granting them a competitive edge.
– Customization. 3D printing is a revolutionary process that takes digital designs and transforms them into physical objects, layer by layer. This unique characteristic allows for incredible customization. No matter how complex the design may be, 3D printers can create molds that perfectly match the specifications. This is particularly advantageous for industries or applications that require unique or limited-run molds, as it eliminates the high costs and challenges associated with traditional production methods.
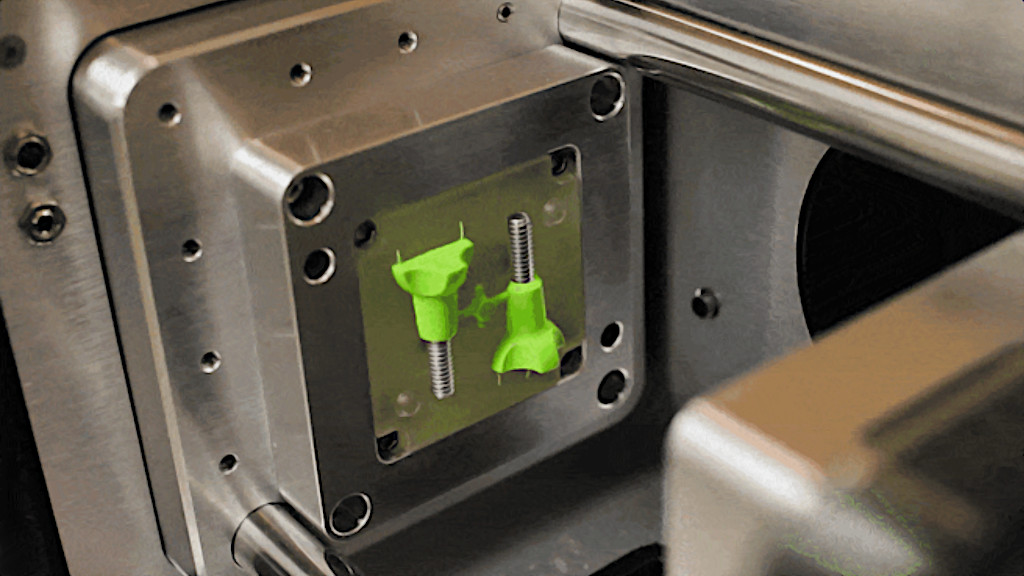
Image: Micromolder
– Prototyping. In the traditional mold-making process, prototyping can be both costly and time-consuming. However, with 3D printing, manufacturers can create prototype molds to test their designs. This rapid prototyping ensures that any design flaws or imperfections are identified early in the process. Multiple iterations of a prototype can also be produced in quick succession, allowing for iterative testing and refining, thus ensuring the final mold is of the highest quality.
– Lower Costs. 3D printing has made mold manufacturing cost-effective because of its additive manufacturing approach. Unlike traditional methods that often result in significant material wastage and require specialized tooling, 3D printing takes an additive approach where it only adds material where necessary, minimizing waste. Additionally, with 3D printers working directly from digital files, expensive tooling or setup costs become unnecessary. As a result, it reduces material and operational expenses, while making products affordable for the end consumers.
Challenges and Limitations
Although it offers many advantages in mold manufacturing, 3D printing faces a number of challenges and limitations.
– Material Restrictions. One of the biggest challenges in 3D printing for mold manufacturing is the limited options for materials. Although there has been progress in expanding material choices, they still can’t match the variety and properties found in traditional mold manufacturing. Certain applications require heat resistance, strength, and durability that many 3D printed materials may lack when compared to traditional metals and composites. Due to this limitation, the range of scenarios where 3D printed molds can be effectively used is restricted.
– Resolution and Tolerance: Precision holds great importance in mold manufacturing. Although high-end 3D printers can achieve remarkable resolution, they may not always meet the exact tolerances necessary for certain mold applications. The layer by layer process of 3D printing sometimes results in minor imperfections and inconsistencies in the final product, which proves unsatisfactory in industries that rely on high tolerances. Achieving these tolerances through post-processing of 3D printed molds can be labor-intensive and may compromise some of the speed benefits associated with the printing process.
– Scale. 3D printing technology is restricted by the build volume of the printer. This means that there’s a limit to the size of the molds that can be directly printed. For larger mold requirements, the mold must either be printed in parts and assembled, which can introduce joints and seams, or manufacturers might have to revert to traditional mold-making methods. While 3D printing is cost-effective for smaller runs and prototypes, it might not be as economical for large-scale, high-volume mold production due to the slower additive process compared to subtractive methods like CNC machining.
Case Studies and Applications
3D printing has been adopted by many industries to improve the efficiency of mold manufacturing. Some of the industries leading in the adoption and integration of 3D printing are automotive plastic injection molding, aerospace and medical sectors. Here are some case studies of how 3D printing has been used to improve the manufacturing processes in these industries.
Industrial Examples
– Automotive Industry. The automotive sector has benefitted in the integration of 3D printing greatly. Big players like BMW and Ford have embraced this technology, using 3D printed molds to create various components for vehicle interiors. For instance, they use these molds when producing door panels and vents. By doing so, these companies have successfully shortened the lead times for prototyping and small-scale production runs. This not only allows them to be more responsive during design iterations but also promotes greater agility in their overall operations.
– Aerospace. In a domain that prioritizes precision and lightweight components, aerospace giants like Airbus and Boeing have embraced the use of 3D printed molds for specific cabin parts and components. These innovative molds enable the creation of intricate and lightweight pieces, contributing to an overall reduction in aircraft weight while maintaining exceptional strength.
Innovative Solutions
– Complex Geometries. Medical companies have experienced many advantages through the adoption of 3D printing. This revolutionary technology has enabled swift modeling and simulation of complex geometries in medical devices, overcoming the obstacles posed by traditional mold-making techniques. By embracing 3D printing, these companies can fabricate precision molds that precisely capture all design intricacies ensuring successful production of high-accuracy devices.
– Rapid Iteration in Consumer Electronics. Tech manufacturing companies that aim to create unique ergonomic designs for handheld devices encounter challenges when using traditional mold methods for prototyping due to frequent design changes. However, by leveraging 3D printing technology, these companies can quickly produce and iterate molds. This allows them to test various design versions in real-time and ultimately develop optimized products for the market.
Conclusion
The integration of 3D printing technology in mold manufacturing has marked a new era of innovation and efficiency. Its transformative capabilities expedite production timelines, introduce unprecedented customization options, and offer cost-effective solutions for prototyping and small batch productions. However, it’s important to note that certain limitations such as material restrictions, resolution challenges, and scalability issues. Despite these obstacles, companies like TDL Mold are at the forefront of this evolution, harnessing the full potential of 3D printing in mold manufacturing. TDL Mold is a plastic injection molding company that combines traditional craftsmanship with cutting-edge technology to shape the future of mold manufacturing.
Read more: Injection Molding Guides and Reviews
Injection molding has been around for a while now. In the field of manufacturing, particularly in mass production, it’s commonly regarded as a preferred option. Here, you will find guides and reviews featuring this manufacturing process.
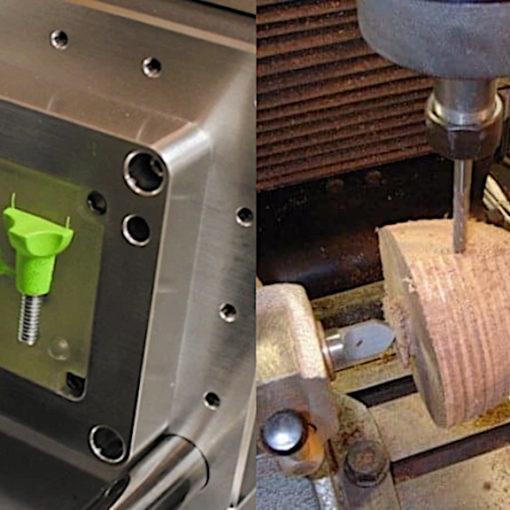




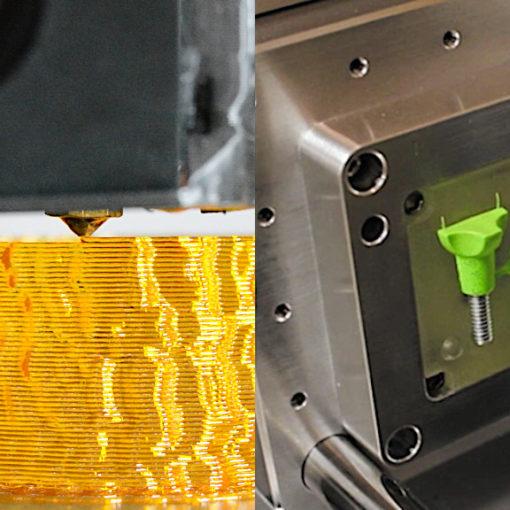


Traditional methods of mold production often involve time-consuming processes and high costs. However, with the advent of 3D printing technology, the landscape has changed dramatically.